publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order.
2024
-
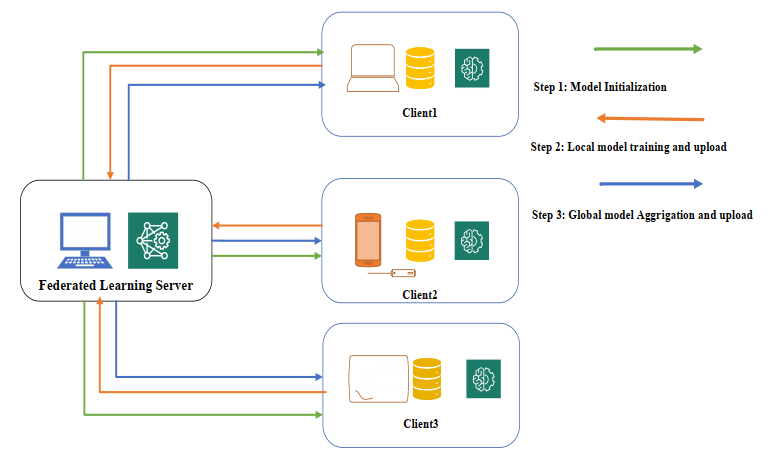 Federated Learning: Attacks, Defenses, Opportunities, and ChallengesGhazaleh Shirvani, Saeid Ghasemshirazi, and Behzad BeigzadehIn 2024 11th International Symposium on Telecommunications (IST) , 2024
Federated Learning: Attacks, Defenses, Opportunities, and ChallengesGhazaleh Shirvani, Saeid Ghasemshirazi, and Behzad BeigzadehIn 2024 11th International Symposium on Telecommunications (IST) , 2024Using dispersed data and training, federated learning (FL) moves AI capabilities to edge devices or does tasks locally. Many consider FL the start of a new era in AI, yet it is still immature. FL has not garnered the community’s trust since its security and privacy implications are controversial. FL’s security and privacy concerns must be discovered, analyzed, and recorded before widespread usage and adoption. A solid comprehension of risk variables allows an FL practitioner to construct a secure environment and provide researchers with a clear perspective of potential study fields, making FL the best solution in situations where security and privacy are primary issues. This research aims to deliver a complete overview of FL’s security and privacy features to help bridge the gap between current federated AI and broad adoption in the future. In this paper, we present a comprehensive overview of the attack surface to investigate FL’s existing challenges and defense measures to evaluate its robustness and reliability. According to our study, security concerns regarding FL are more frequent than privacy issues. Communication bottlenecks, poisoning, and backdoor attacks represent FL’s privacy’s most significant security threats. In the final part, we detail future research that will assist FL in adapting to real-world settings.
2023
- preprint
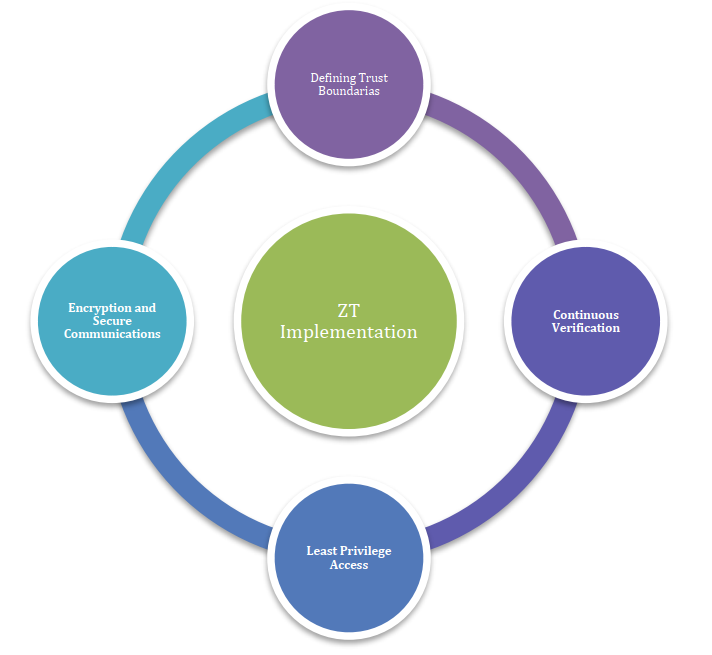 Zero Trust: Applications, Challenges, and OpportunitiesSaeid Ghasemshirazi, Ghazaleh Shirvani, and Mohammad Ali AlipourarXiv preprint arXiv:2309.03582, 2023
Zero Trust: Applications, Challenges, and OpportunitiesSaeid Ghasemshirazi, Ghazaleh Shirvani, and Mohammad Ali AlipourarXiv preprint arXiv:2309.03582, 2023The escalating complexity of cybersecurity threats necessitates innovative approaches to safeguard digital assets and sensitive information. The Zero Trust paradigm offers a transformative solution by challenging conventional security models and emphasizing continuous verification and least privilege access. This survey comprehensively explores the theoretical foundations, practical implementations, applications, challenges, and future trends of Zero Trust. Through meticulous analysis, we highlight the relevance of Zero Trust in securing cloud environments, facilitating remote work, and protecting the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. While cultural barriers and technical complexities present challenges, their mitigation unlocks Zero Trust’s potential. Integrating Zero Trust with emerging technologies like AI and machine learning augments its efficacy, promising a dynamic and responsive security landscape. Embracing Zero Trust empowers organizations to navigate the ever-evolving cybersecurity realm with resilience and adaptability, redefining trust in the digital age.
@article{ghasemshirazi2023zero, title = {Zero Trust: Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities}, author = {Ghasemshirazi, Saeid and Shirvani, Ghazaleh and Alipour, Mohammad Ali}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.03582}, year = {2023}, }
2022
- preprint
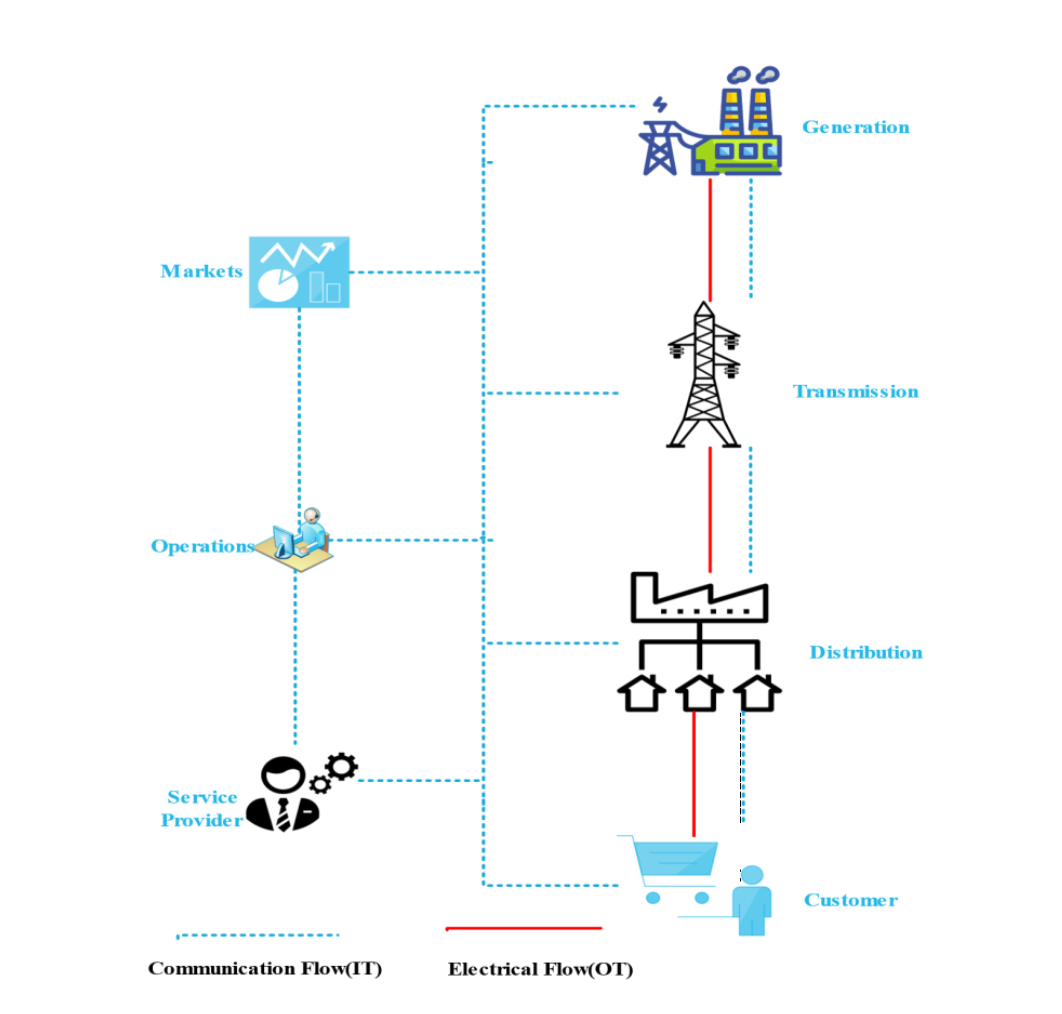 Enabling a Zero Trust Architecture in a 5G-enabled Smart GridMohammad Ali Alipour, Saeid Ghasemshirazi, and Ghazaleh ShirvaniarXiv preprint arXiv:2210.01739, 2022
Enabling a Zero Trust Architecture in a 5G-enabled Smart GridMohammad Ali Alipour, Saeid Ghasemshirazi, and Ghazaleh ShirvaniarXiv preprint arXiv:2210.01739, 2022One of the most promising applications of the IoT is the Smart Grid (SG). Integrating SG’s data communications network into the power grid allows for gathering and analyzing information from power lines, distribution power stations, and end users. A smart grid (SG) requires a fast and dependable connection to provide real-time monitoring through the IoT. Hence 5G could be considered a catalyst for upgrading the existing power grid systems. Nonetheless, the additional attack surface of information infrastructure has been brought about by the widespread adoption of ubiquitous connectivity in 5G, to which the typical information security system in the smart grid cannot respond promptly. Therefore, guaranteeing the Privacy and Security of a network in a threatening, ever-changing environment requires groundbreaking architectures that go well beyond the limitations of traditional, static security measures. With" Continuous Identity Authentication and Dynamic Access Control" as its foundation, this article analyzes the Zero Trust (ZT) architecture specific to the power system of IoT and uses that knowledge to develop a security protection architecture.
@article{alipour2022enabling, title = {Enabling a Zero Trust Architecture in a 5G-enabled Smart Grid}, author = {Alipour, Mohammad Ali and Ghasemshirazi, Saeid and Shirvani, Ghazaleh}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.01739}, year = {2022}, }
2021
- CSICC
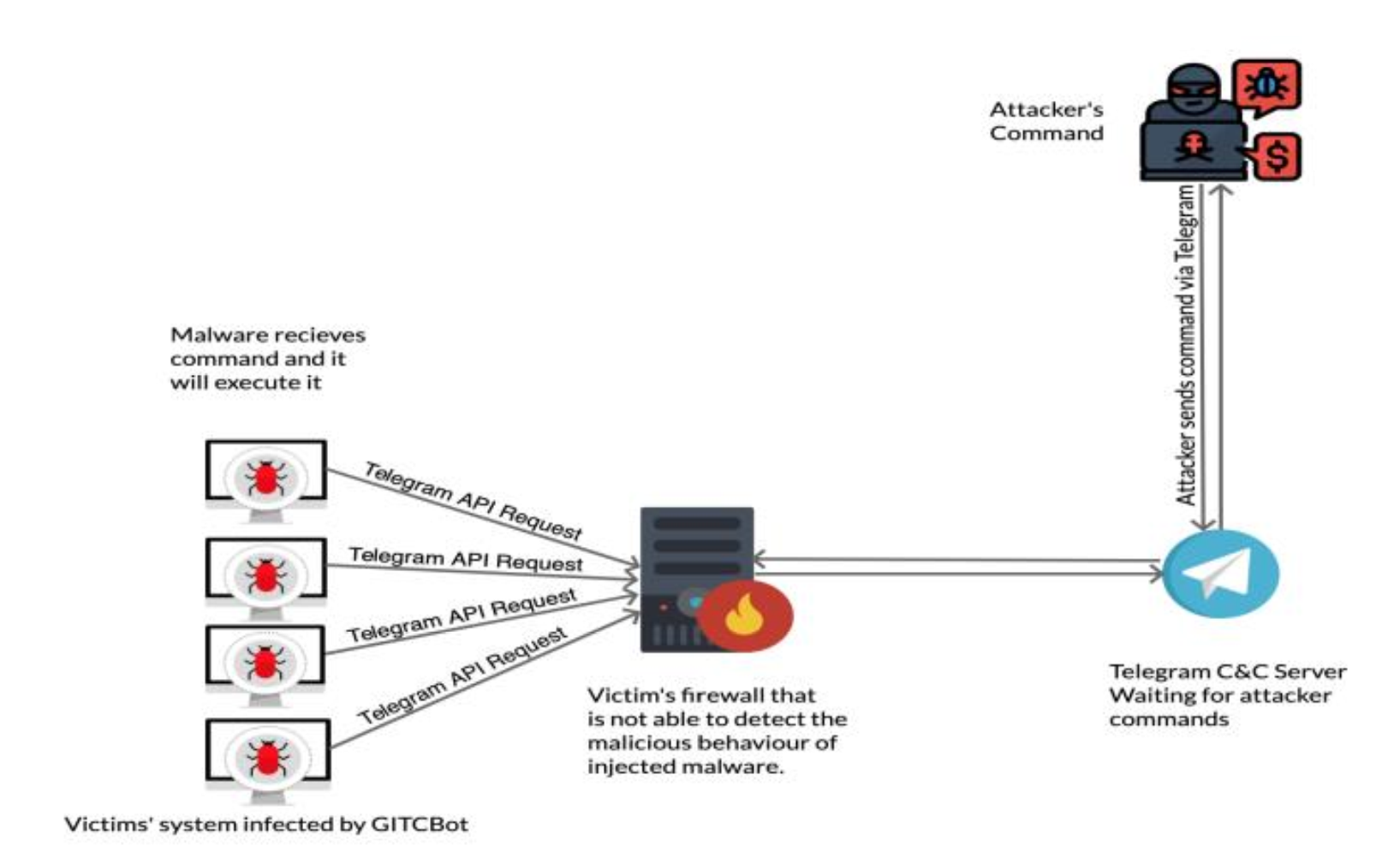 Gitcbot: A novel approach for the next generation of c&c malwareSaeid Ghasemshirazi, and Ghazaleh ShirvaniIn 2021 26th International Computer Conference, Computer Society of Iran (CSICC) , 2021
Gitcbot: A novel approach for the next generation of c&c malwareSaeid Ghasemshirazi, and Ghazaleh ShirvaniIn 2021 26th International Computer Conference, Computer Society of Iran (CSICC) , 2021Online Social Networks (OSNs) attracted millions of users in the world. OSNs made adversaries more passionate to create malware variants to subvert the cyber defence of OSNs. Through various threat vectors, adversaries persuasively lure OSN users into installing malware on their devices at an enormous scale. One of the most horrendous forms of named malware is OSNs’ botnets that conceal C&C information using OSNs’ accounts of unaware users. In this paper, we present GITC (Ghost In The Cloud), which uses Telegram as a C&C server to communicate with threat actors and access targets’ information in an undetectable way. Furthermore, we present our implementation of GITC. We show how GITC uses the encrypted telegram Application Programming Interface (API) to cover up records of the adversary connections to the target, and we discuss why current intrusion detection systems cannot detect GITC. In the end, we run some sets of experiments that confirm the feasibility of GITC.
@inproceedings{ghasemshirazi2021gitcbot, title = {Gitcbot: A novel approach for the next generation of c\&c malware}, author = {Ghasemshirazi, Saeid and Shirvani, Ghazaleh}, booktitle = {2021 26th International Computer Conference, Computer Society of Iran (CSICC)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2021}, organization = {IEEE}, } - ICWR
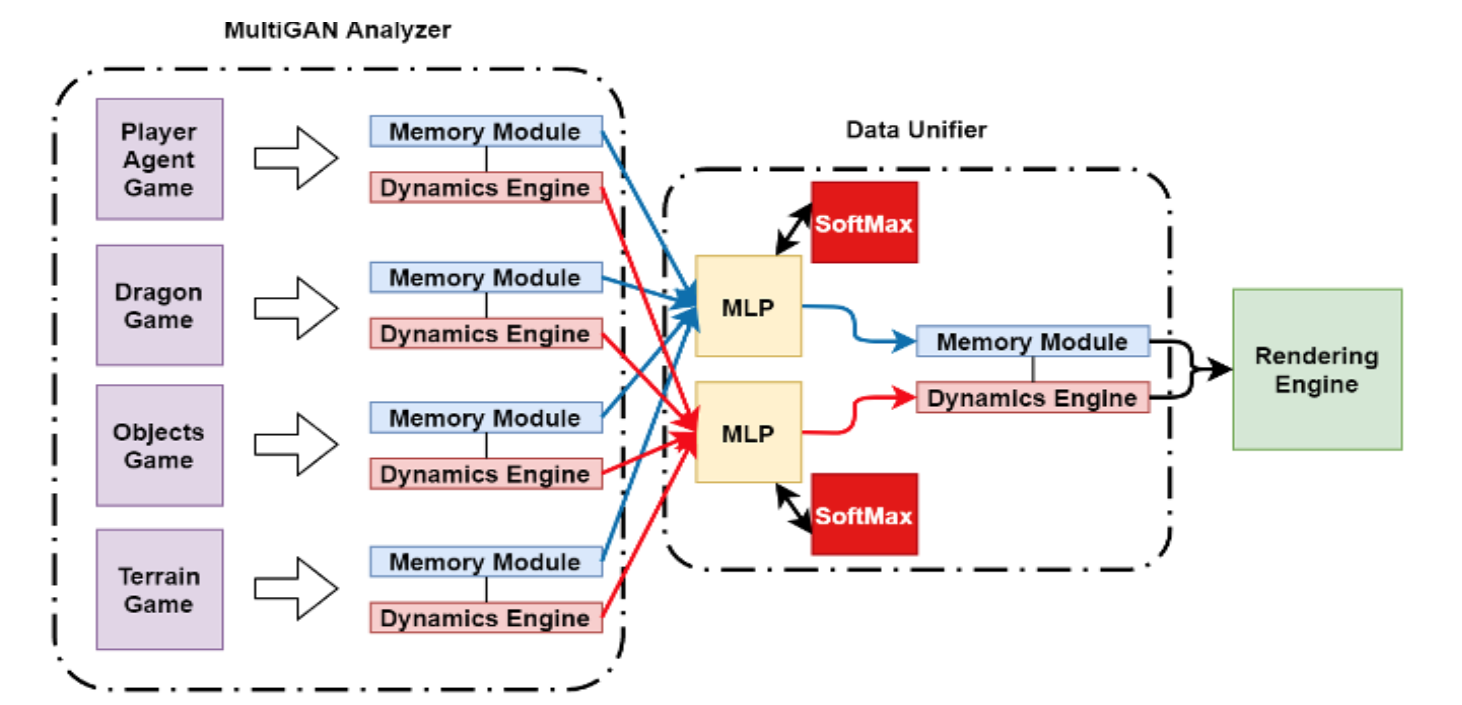 MC-GAN: A Reimplementation of GameGAN With a Gaming PerspectiveSaeid Ghasemshirazi, Ghazaleh Shirvani, and Saeed RaisiIn 2021 7th International Conference on Web Research (ICWR) , 2021
MC-GAN: A Reimplementation of GameGAN With a Gaming PerspectiveSaeid Ghasemshirazi, Ghazaleh Shirvani, and Saeed RaisiIn 2021 7th International Conference on Web Research (ICWR) , 2021Creating games is a costly process involving tons of vigorous efforts, time, and resources. Different game engines were introduced to facilitate the game-making process, such as Unreal Engine, Unity, and Godot. However, despite the advent of game engines, the vacuum of automatically creating new games by computers was still felt. With artificial intelligence (AI) development and its growing presence in the industry, game developers made a new game development branch using AI. One of the essential steps in this context was the introduction of GameGAN, which inspired us for this article. Here we propose Multi-Class GamgeGan(MC-GAN), a starting point for the next generation of game engines based on GameGAN. In addition, MC-GAN is capable of classifying each desired game element and even changing its class to change the element’s nature (e.g., MC-GAN can change static elements to dynamic ones …
@inproceedings{ghasemshirazi2021mc, title = {MC-GAN: A Reimplementation of GameGAN With a Gaming Perspective}, author = {Ghasemshirazi, Saeid and Shirvani, Ghazaleh and Raisi, Saeed}, booktitle = {2021 7th International Conference on Web Research (ICWR)}, pages = {323--328}, year = {2021}, organization = {IEEE} } - preprint
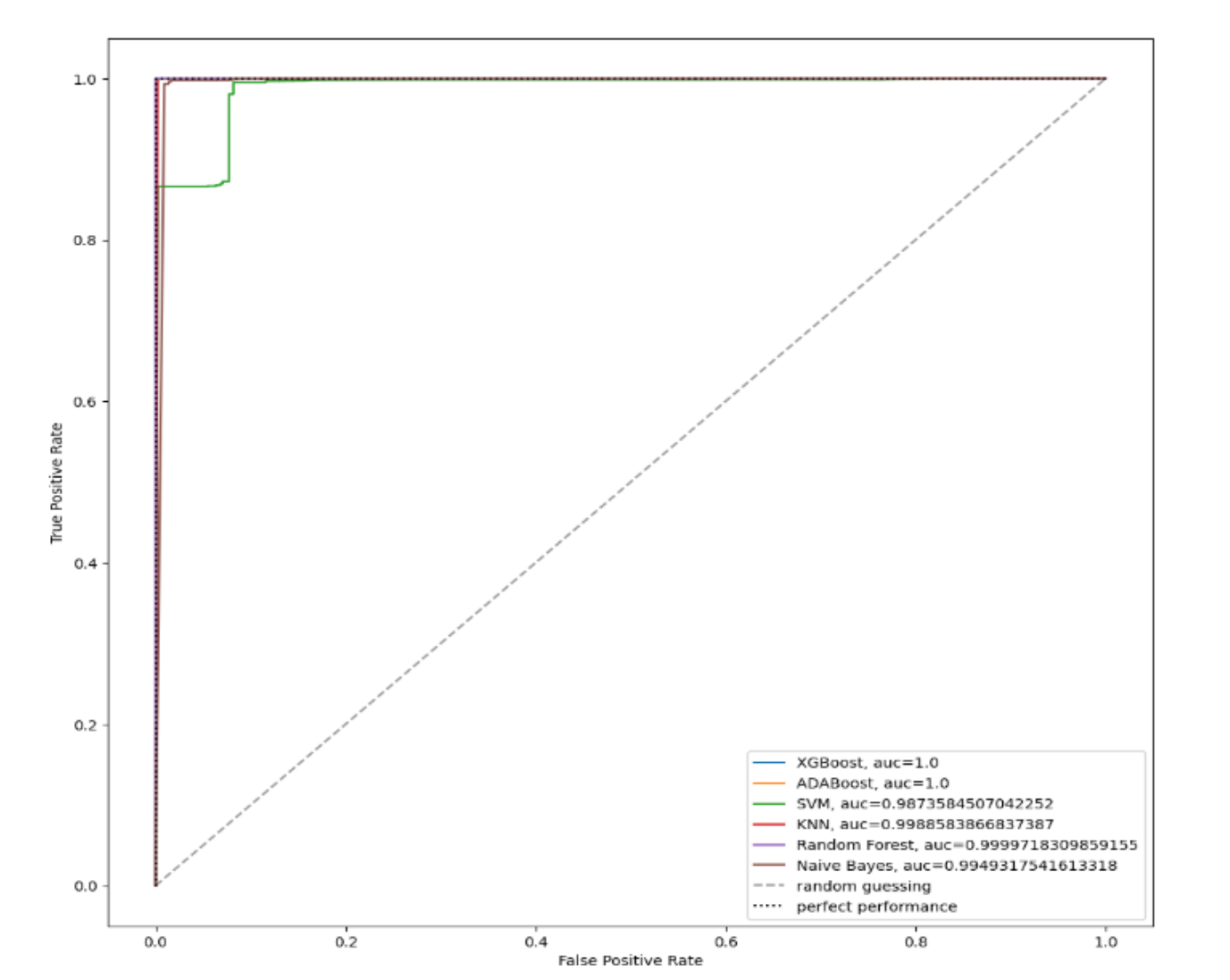 A Machine Learning approach for DDoS detection on IoT devicesAlireza Seifousadati, Saeid Ghasemshirazi, and Mohammad FathianarXiv preprint arXiv:2110.14911, 2021
A Machine Learning approach for DDoS detection on IoT devicesAlireza Seifousadati, Saeid Ghasemshirazi, and Mohammad FathianarXiv preprint arXiv:2110.14911, 2021In the current world, the Internet is being used almost everywhere. With the rise of IoT technology, which is one of the most used technologies, billions of IoT devices are interconnected over the Internet. However, DoS/DDoS attacks are the most frequent and perilous threat to this growing technology. New types of DDoS attacks are highly advanced and complicated, and it is almost impossible to detect or mitigate by the existing intrusion detection systems and traditional methods. Fortunately, Big Data, Data mining, and Machine Learning technologies make it possible to detect DDoS traffic effectively. This paper suggests a DDoS detection model based on data mining and machine learning techniques. For writing this paper, the latest available Dataset, CICDDoS2019, experimented with the most popular machine learning algorithms and specified the most correlated features with predicted classes are being used. It is discovered that AdaBoost and XGBoost were extraordinarily accurate and correctly predicted the type of network traffic with 100% accuracy. Future research can be extended by enhancing the model for multiclassification of different DDoS attack types and testing hybrid algorithms and newer datasets on this model.
@article{seifousadati2021machine, title = {A Machine Learning approach for DDoS detection on IoT devices}, author = {Seifousadati, Alireza and Ghasemshirazi, Saeid and Fathian, Mohammad}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.14911}, year = {2021}, } - SGC
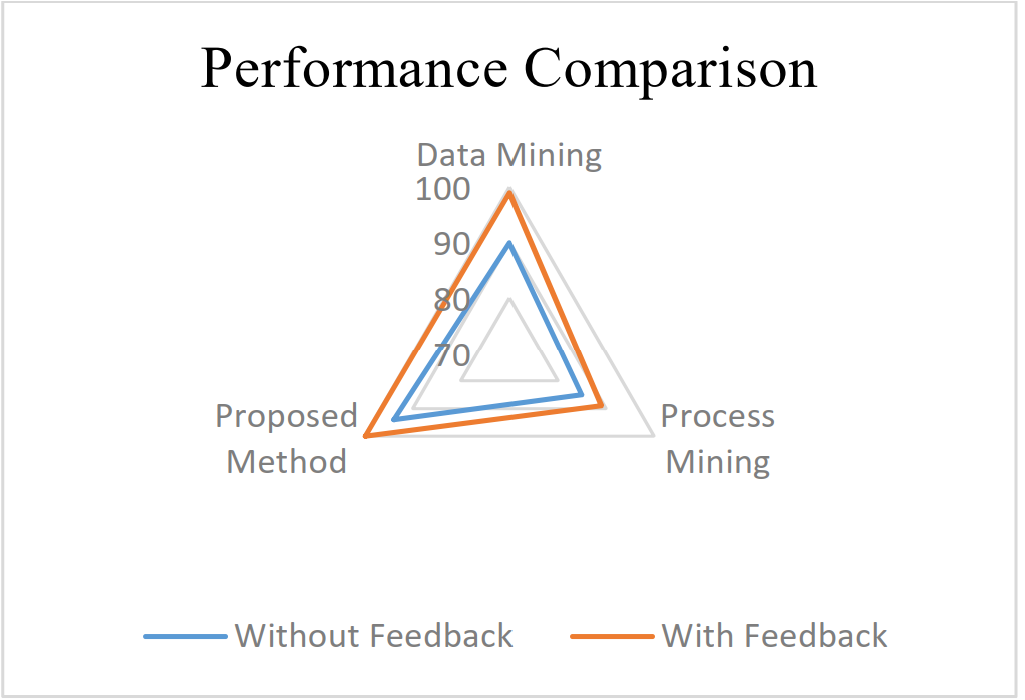 IoT-Shield: A Novel DDoS Detection Approach for IoT-Based DevicesGhazaleh Shirvani, Saeid Ghasemshirazi, and Behzad BeigzadehIn 2021 11th Smart Grid Conference (SGC) , 2021
IoT-Shield: A Novel DDoS Detection Approach for IoT-Based DevicesGhazaleh Shirvani, Saeid Ghasemshirazi, and Behzad BeigzadehIn 2021 11th Smart Grid Conference (SGC) , 2021The widespread deployment of sensors and linked items contributes to the rising interest in the Internet-of-Things (IoT). These are used in conjunction with other Online services to develop highly sophisticated and profitable cloud-based services. Despite significant attempts to secure them, security management remains a crucial problem for these devices, Because of their intricacy, heterogeneous nature, and resource constraints. This paper presents IoT-Shield, a data mining technique that coincides with a process mining approach for identifying misbehavior in of the kind. IoT-Shield enables the characterization of IoT devices’ behavioral models and the detection of possible threats, even in the presence of diverse protocols and platforms. The underlying architecture and components are then described and formalized, and a proof-of-concept prototype is detailed. A real-world traffic dataset known as KDD-NSL is …
@inproceedings{shirvani2021iot, title = {IoT-Shield: A Novel DDoS Detection Approach for IoT-Based Devices}, author = {Shirvani, Ghazaleh and Ghasemshirazi, Saeid and Beigzadeh, Behzad}, booktitle = {2021 11th Smart Grid Conference (SGC)}, pages = {1--7}, year = {2021}, organization = {IEEE}, } - IKT
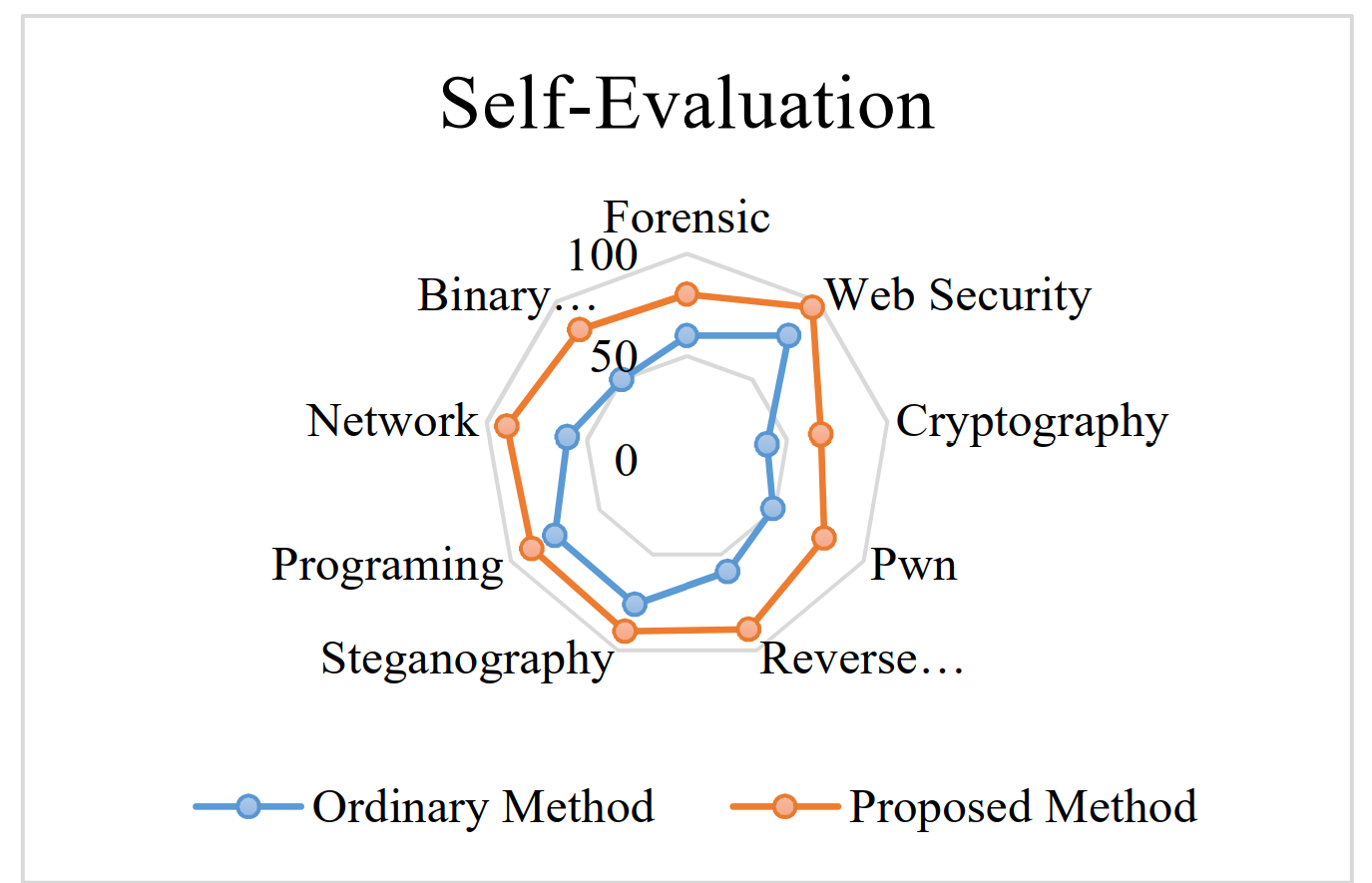 UltraLearn: Next-Generation CyberSecurity Learning PlatformSaeed Raisi, Saeid Ghasemshirazi, and Ghazaleh ShirvaniIn 2021 12th International Conference on Information and Knowledge Technology (IKT) , 2021
UltraLearn: Next-Generation CyberSecurity Learning PlatformSaeed Raisi, Saeid Ghasemshirazi, and Ghazaleh ShirvaniIn 2021 12th International Conference on Information and Knowledge Technology (IKT) , 2021Learning was always an essential part of our lives to acquire knowledge and move forward. However, the increasing wages of on-campus learning leads to an increasing need for an alternate way of learning. With the outbreak of COVID-19, people needed to stay at home for safety. Therefore, finding an answer to this need became more dominant. Another major problem, especially in the ongoing decade, is the lack of enough cybersecurity knowledge by the common folk. This paper aims to look at a new platform that is carefully designed to teach cybersecurity to learners with any background. We design this system using gamification to increase the efficiency of learning. Because modern technologies are ubiquitous in our lives, particularly during the coronavirus outbreak, including practical work in teaching will be quite beneficial. The practical activity has a clear advantage, such as promoting experimental learning and improving student abilities and skills for the future professional career. Finally, we assess this method with a classic learning approach using two different groups.
@inproceedings{raisi2021ultralearn, title = {UltraLearn: Next-Generation CyberSecurity Learning Platform}, author = {Raisi, Saeed and Ghasemshirazi, Saeid and Shirvani, Ghazaleh}, booktitle = {2021 12th International Conference on Information and Knowledge Technology (IKT)}, pages = {83--88}, year = {2021}, organization = {IEEE} }